Evolution and opportunities of the PRF in Europe
Technical partner of the Centre Spanish of plastics10/01/2008
It was estimated that in 2002 the world industry of PRF produced pieces for a value of € 41,500 million and a cost of 33 billion, of which 29 per cent related to raw materials and equipment9 per cent to intermediate products, 5 percent to distributors and the 57 percent to costs of transformation.
40% Of this value was produced in North America, 35 per cent in Europe, 22 per cent in Asia and only 3 per cent in the rest of the world. With regard to its industrial uses, they reached all sectors, but the four dominant markets were: Automotive (23 percent), Civil Construction (21%), Aviation (17%) and sports and recreation (9%). The other 30 percent was very divided between industrial equipment, shipbuilding, electricity, electronics, wind energy, medicine, railway and consumer goods.
Its annual growth worldwide is expected to be 4-5 per cent, but with higher growth in some sectors, such as wind energy (18%), shipbuilding (7 percent), or electronic (5 percent). In Europe and North America were expected maximum of 4 percent growth, while in Asia would be of 10.6 per cent, emphasizing above India (14.5) and China (9.5 per cent), while only Japan would grow 3.5 percent.
With regard to the main strategies that should influence these forecasts of growth, we highlight the following four:
- Innovation, both in materials, equipment and working methods, and applications.
- Replacement of traditional materials for composites PRF, in order to improve their applications, design, aesthetics and cost.
- Increased consumption of parts where the market already accepted that the manufactured with PRF are more satisfactory for your needs.
- Adapted to the legal regulations affecting manufacturing, use and recycling of composites PRF in each country.
European growth
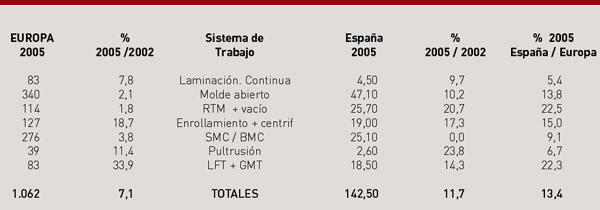
The annual total growth have not been of 4 percent as expected, nor even in the year 2004, when it got a 3.2 per cent, but that growth continued during the past three years has beenWhile the building still growing in Europe, and the relocation of some factories of cars and electrical equipment have forced move also those of some components out of Europe. Also the beginning of the unstoppable global escalation of oil prices, slowed further growth in 2005, but these are still positive. The overall growth in the production of PRF in Europe, over the three years 2002-2005 has been from 7.1 per cent.
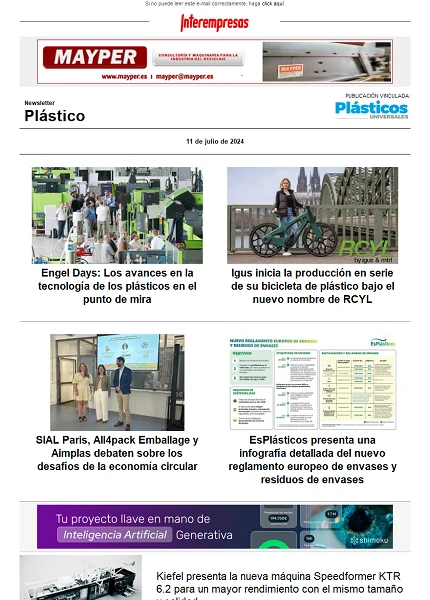
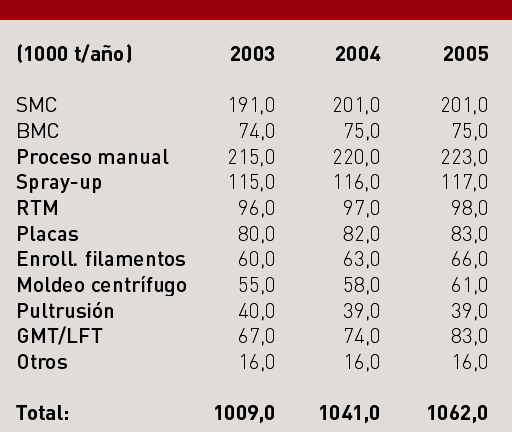
There is great disparity in what is in the individual growth of each family of transformation according to methods used. The interannual variations that have had these growth for each of the families are represented in the chart below. Here is where you can better see how the General problems of every market affect the various productive sectors
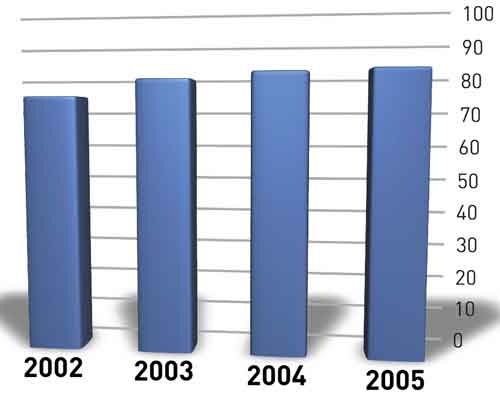
SMC / BMC
Production of BMC grew together in 2004, despite the loss of its use in electrical components for construction, factor that had already affected his production of the previous year, and that was aggravated in 2005, which is why this year went down.
Manual techniques to mold open and closed mold
The interesting thing is that also consolidates the use of these techniques in their traditional applications, having been slowed technological change of mold open mold closed fearing to renege on the levels of styrene permitted in plant. In addition, grow moderately as the contact as the simultaneous projection molding.
The growth observed these years in RTM and other techniques to closed mold, are now, mainly, new projects based on the quality and speed that are achieved with these interesting technologies, growing more than open mold.
Plates in continuous
The wavy plate is harder to know if he grew up, their manufacturers used enough quantities of resins and fibers of quality difficult to control.
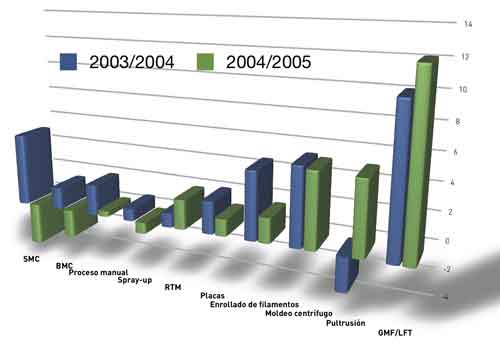
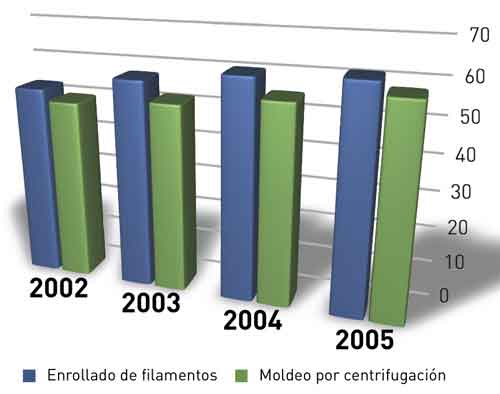
Pipes and tanks
Not only drain piping, but that also appeared new industrial projects, that they have driven its growth in 2005 and expected to continue in the coming years, as the work of standardization, that for years to take up the manufacturers of pipes and tanksIt has achieved credibility among the construction companies, employing them to technically solve the challenges of the new legislation on chemicals and water conduction.
It is worth noting that the method of mechanical splices both of centrifugation, grow healthy in their respective markets, as we see in the graphic attached.
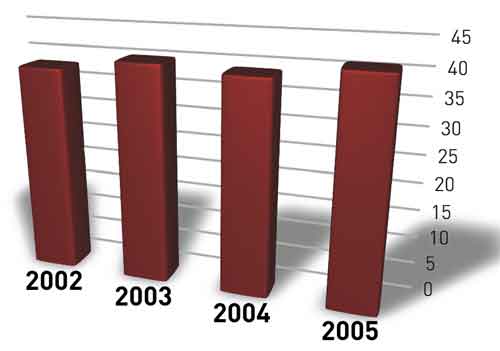
Pultrusion
New developments in bridges with ability to accept heavy traffic have been news up in daily newspapers, because the great appeal of these bridges is that maintenance is significantly lower than that of the reinforced concrete and better resistant to weathering.
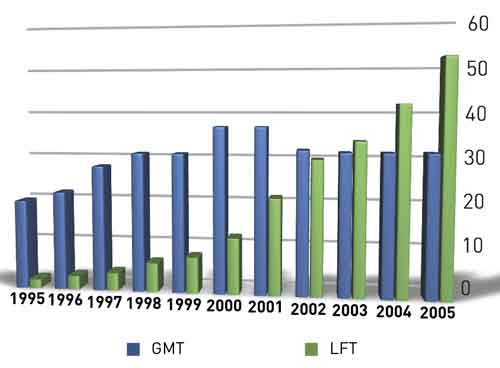
GMT /LFT
Plastics reinforced with natural fibers
The figures for the tonnage of PRF made with natural fibers gathered them Institute Nova (Hürth) of their manufacturers. Unfortunately the last data gathering took place in 2003, which is why we do not have recent data. The trend of recent years was a moderate growth. We hope that this trend will increase in the next.
More recent is the use of wood as reinforcement for thermoplastic fibre. These composites (WPC) wood can mold injection easily and are mainly used in construction. They will be a very interesting material for the manufacture of furniture.
Plastics reinforced with carbon fiber
More than half of this consumption is for the aviation industry. However, there are expectations real that is used in the automotive industry via SMC reinforced with carbon fiber.
The growth in Spain
The result is that in 2005, based on data that has just published the Spanish Center of plastics (4), the PRF grew at a 3.5% Spain, (from them, the single unsaturated polyester grew by 1.5 per cent)(, the rest was due to other polymers), twice in the whole of Europe, and during the last three years it is estimated that here raised production by 11.7 per cent, far more than the average of EU as a whole.
In the table no. 2 have compared the results of the PRF production in both sets, both for the production of the 2005 growth both have had on the three-year period 2002-2005. These data are obtained by different organizations, whose classification criteria may not coincide and therefore your comparison is dubious, but the evolution of each of the sets that tells us how have grown each of them.
In Spain there is already a 13 per cent of the total European PRF and also which is transformed to open cast (contact and projection), we are above the European average in pipe (twisting + centrifugation), thermoplastics, and manual processing closed mold (RTM + vacuum and other).
Instead transforms below the average for SMC / BMC and pultrusion (albeit a minority technology in Spain, growing very well). Continuous lamination, Spanish data reflects only those of corrugated iron, already to the production of sheet flat continuous joins of the moulding by contact, which is why the Spanish figure is not comparable with the European.
Highlights in Spain notable growths that are experienced consumption of composites made with phenolic resins for fireproof in railway parts, and especially for aeronautical epoxide resins, sports and blade wind. In this field, Spain has become produce 2 percent of its electricity with wind turbines in the year 2000, to 7.5 per cent in 2005. Also here are replaced mills by other more powerful, to be used as blades of up to 47 m also increases wind farms, because the Spanish renewable energy plan with wind energy producing 20,000 MW in 2010.
Also in Spain, the consumption of carbon fiber and other fibers have grown over the glass fibre. All this indicates that the Spanish transformation of FRF as well as grow well, was also known to adapt to technological change.
European strategies
Since then, the promotion of innovation, has been the basic pillar for growth output in all applications of the PRF. R & d incentives granted by the EU and by each of its States members, to support new projects presented by the companies, with the help of universities, technological centres and associations of companies from different countries of the EUthey have been very positive and we believe that they will continue to be basic in the coming years. Parliament adopted the framework programme for competitiveness and innovation (CIP), endowing it of 3.621 million euros for the period 2007-2013 and that includes three specific programmes:
• Enable small businesses to invest in innovation,
• Promote energy efficiency
• Encourage the optimized use of the information technologies and communications
We are in full VII adjustment of the IPC (16), so now is the time that the companies with new innovation projects, either on their own or from their associations, soon begin contacts with University or technology centresSpanish community, and, where they can find support for their ideas, and make proposals that are appropriate to the orientation of the programme.
In Spain, also the zenith of the Cedeti programs have successfully supported the innovative development of many small and medium enterprises, and will serve as a new Unipyme loans to finance up to 100 percent of r & d programmes that subscribe to small and medium-sized enterprises with universities and public research organizations.
The replacement of parts made of traditional materials by others manufactured with PRF requires a lot of associations of entrepreneurs in the sector. First to normalize the PRF parts, and then to compare them, technically, to those made with materials in use and demonstrate its advantages. Are these associations of manufacturers which have come to the centers of standardization - Aenor in the case of Spain - to apply for the transposition of European standards to our legislation or even request to start new rules, if there is no European legislation covering the field of development, and subsequently, each company has due conduct trials needed to prove the quality of their products. It is worth emphasising the efforts they have made Spanish manufacturers of pipe PRF (Asetub partners) on standardisation and trials, to ensure that some of the major construction of public works fully trust in its products to improve the channelling of all type of fluids.
To increase the consumption of parts redesigned with PRF, is required, that that these products are well defined by standards, testing and certification in some cases, there are technological advocacy among the technicians of consumer companies and the Administration, and informative campaigns for the public in general, in a way that have comparative criteria global when choosing the most suitable to your case. Here is contributing to a large extent the support of the major exhibitions and technical workshops of PRF are organized in Europe, which now include forums for opinion, where processing companies and users of a given market exchange their achievements and needs. Also these days include the awards to the best solutions presented this year in raw materials, equipment or finished parts.
In the last JEC meeting rooms (5) have been organized, in parallel with the exhibition, six encounter between processing companies and user forums: boating, land transport, aerospace, construction, natural fibres and automotive, and seven awards were called to the innovation, whose concession became public and was held at the end of the first day, with the assistance of all visitors to the contest.
Also some national federations of PRF, as the influential German AVK, has included in its international conferences of recent years, their awards for innovation in three categories: Industrial, environmental, and universities, with a huge success, because manage to make more fluid contacts between technical and University researchers from companies who attend its conferences.
Get adapted to the current legislation needs not only of the joint effort of the entire sector, including transformers, policy makers and manufacturers of raw materials and equipment, to develop and implement new clean energy technology, but also support the image that this sector is committed to the sustainable development of a serious and effective manner. Without such initiatives, which must be made available to the public, it is difficult to negotiate with the authorities the necessary aid for its implementation.
EuCIA, the European Association of PRF, has promoted the concept of "Green label" to support recycling products no longer in use in Europe., through the ECRC organization, that deals with collect, separate and treat the waste of its associate companies and subsequently find their recycling. ECRC France has already put in place a system of collection of PRF pieces out of use, separation and treatment in three shredder plants, strategically distributed throughout the country and from which caters to five French cement, who already use these materials in some of their formulas to reduce energy expenditure with the combustion of polymers and reuse fibres and other inorganic components of this waste as raw materials (6).
Opportunities that have triumphed
Construction
2 Rods of resin reinforced with fibers of carbon or of basalt to replace steel in reinforced concrete. Project presented Black Bull ACE and four partners (Norway) and Kaameny Vek (Russia). It's a reinforcement made by 30 times faster process which the pultrusion and allowing coating the surface of these rods with material granular embedded in resin, to facilitate the adherence of the concrete to the fibers. Its goal is to eliminate corrosion of steel in reinforced concrete, to increase their useful life. It had its commercial release last year with the construction of 3 floating pontoons of 13 x 3 m2 for use in a Baltic port. He has won the JEC 2006 Award for construction (8).
3. Large-diameter pipes used in desaladoras plants and combined cycle. The plan Spanish to correct water imbalances is based in new desaladoras plants, in which on the basis of brackish water is achieved, by reverse osmosis, its safe for human consumption and irrigation. Both making salt water, and the return to the sea of wastewater with high concentration of salt, are being made through wealth FRP pipes (up to 3,200 mm. in diameter), completely watertight and resistant to corrosion. The subsequent conduct of drinking water to their areas of use will also with GFRP pipes, by their tightness, which avoids the enormous losses that had previous piping. Also in the combined cycle thermal power stations are used FRP pipes, usually buried, greater rigidity and with diameters between 1,500 to 3,200 mm. Therefore, the continued growth of this application is guaranteed for the coming years. In photography, courtesy of Protesa, can see a detail of the installation of some 3,200 mm pipes


Automotive
Also Mr. k. Heidenreich of BMW at the recent seminar on innovation with SMC in automotive held at Landshut (Germany) (9), explained details of the pieces which already manufactured in its factory in Dingolfing (Germany) with pintable SMC for body stylesas well as his confidence that the number of these pieces continue to grow. Later we could see the painted line of bodywork made from SMC parts assembled with other metal.
Road transport
They are made with PP and glass fibre roving. They are not oxidized and have a double longitudinal stability than the commonly used steel. Its potential market is very high because in Europe are installed 1.2 million units a year.
6. Implementation of PRF profiles in the manufacture of refrigerating boxes. E. Cañibano and other technical of CIDAUT, recently published in Plasticos Modernos (11) your system to reduce the weight of trucks by 25% (990 Kg) storage boxes, replacing the metal and wood of its structure by PRF profiles produced by pultrusion and using for soil structure, honeycomb panel filled with foam PSto keep the coated by a stratified PRF and thermal insulation. All the tests carried out on the mechanical stability and the freezing capacity of the boxes mounted gave equal to the conventional values, but managed to reduce their weight by nearly a ton, allowing carry greater load and saving on fuel when driving vacuum.
7 Hycoprod, European project for the development of economic production methods for sandwich large monohull structures. This project coordinated by Advanced Railway Research Center (UK) and in which involved 18 partners, including Irizar S Coop. and systems and processes advanced (Spain), received the 2004 JEC innovation award (12) because of its importance to improve the safety of buses and cars without increasing their costs.
Also the JEC 2006 innovation award was for a design to improve security in trains and trams. It's the front piece of the locomotor wagon according to European standard DIN 5560 impact resistant. Developed Júpiter Plast (Dk) and Siemens Mass Transport (D) enterprises. It is structure sandwich core foam and acrylic resin fire, produced by infusion vacuum-resistant. It resists a front force of 30 tons, deforming in a controlled manner to absorb the impact driver to protect and maintain the dimensional stability of the rest of the unit.
Marina
Industry
10. The pilot project Beatrice to install giant wind turbines of 5MW of power (13), on the high seas is based on the experiences made in the North of Germany with e1 larger prototype REpower which installed in 2004, with the collaboration of LM Glasfiber. The project is funded by the EU, and uses the blades LM 61.5P of 61.5 m in length and 17.7 tons of weight, which are now building the 6 necessary to mount the 2 experimental turbines of 5 MW of power that will be installed on the high seas, off the East coast of Scotland, in the Bay of Moray Firth. If the results of five years of tests are positive, the promoter of the project, Taliman Energy, intends installing other 200 wind turbines in the same coasts of the North Sea.
Concluding comments
The increase in consumption as a basis for economic growth has had on the chemical industry as a whole, effects competing over the years. On the one hand, the welfare provided with their improvements to the quality of life of society, have boosted significantly their production volumes and has generated a huge technological development. On the other, their industrial waste, emissions to the environment and chemical accidents have been much more noticeable, and they have been creating a negative social image of the chemical industry in general and that of plastics in particular. In addition, nor the public rated the efforts made by the industry to reduce its negative effects, nor the industry itself has been able to connect well with the society to explain them. The result has been a growing deterioration in the image which society has been formed of chemistry; reaching, in specific cases, create serious problems of survival for some industrial plants.
To address this situation, in 1984, the Canadian Federation of chemical industries launched an initiative called Responsible Care, a program that combined a focused management system to continually improve the performance of the companies in the field of environment and safety and, by another, promote the companies communication with the environment of their plants. In Spain, this program began in 1993 under the name of commitment to progress, and at the global level applies already simultaneously in 52 countries around the world. This program has undoubtedly imposed a new style in public relations. Today the company's medium-size that does not have its open day, channels for dialogue with associations of neighbours and to not become involved in the Affairs of his neighborhood is rare. Also associations of chemicals have been implicated in offering proven information, exposing it in Congress of teachers of secondary education, so that the students do get a not distorted information about the benefits and problems of the chemical industry, and Feique, the Spanish Federation of chemical industries, has edited and distributed the Handbook of communication of risks in the chemical industry, a guide to the communication of crisis, in order to continue to provide transparency.
As a result of this programme, there has been a positive change in public opinion. The European Chemical Industry Council (CEFIC) publishes an annual report that includes the study of image of the area, known as Pan European Survey, which shows the perception of citizens on the chemical industry. The last published report stresses that in 2004, and for the first time, there is a greater number of citizens with positive perception that refusal in Europe, being especially remarkable the progress made in Spain, in our country, more than 60 percent of the population has a perception positive sector and recognized its importance as an engine of generation of wealth, jobs and, through its products, quality of life and well-being of present and future.
To support this new approach, October 25, 2005, he was born in Spain the Forum permanent chemistry and society, supported by the most representative of the industry, Academia, science 10 Spanish institutions and professionals, with the aim of creating a common framework to guide the joint efforts of all institutions involved in the development the chemistry. Subsequently, on 14 March 2006, the Ministry of industry, tourism and commerce was signed the Global Declaration of Responsible Care, a document that introduces new commitments for businesses adhering to program commitment of progress, which was signed by FEIQUE as Business Federation of the Spanish chemical industry (15), and with her Plastics Europe, European Association which brings together almost all multinational companies polymer operating in Spain. Also from the month of June are collecting signatures in all Spain for the Declaration of chemical, a document which is available on the website of the Forum (www.quimicaysociedad.org) which shows the appreciation towards chemistry, from science to industry, as the first engine of progress of humanity. It is an open document to which may join associations, companies and individuals who, after studying it, want to adhere to it. It is worth doing so.
Bibliography
- L Lopez mateo, risks and opportunities for Spanish companies of plastics reinforced, 17th Conference on composite materials, Valencia, 23 and 24 November 2004
- Source: Structure et dinámique des composites, Etude JEC 2004)
- U Bültjer, Production of GRP and Thermosets in Europe 2004-2005. 8Th International AVK-TV Conference, 27-28 September. (2005 Translation into the Spanish in Plasticos Modernos, 596, pag 116, February 2006)
- The plastics Sector, 2005 Edition. Spanish Centre of plastics.
- JEC 2006, Plasticos Modernos, p. 396, May 2006.
- Fons Harber, The green FRP recycling value., seminar on SMC in automotive, organized by AVK, Landshut, Germany, 17-18, May 2006.
- Against the aging of the bridges, chemistry and industry, 563, page 42, March, 2006
- JEC 2006, automotive forum
- Klaus Heidenreich, the SMC in the bodywork of the car. Seminar on SMC in automotive, organized by AVK, Landshut, Germany 17 and 18, May 2006.
- L Lopez Mateo, an interesting application of light RTM. Modern plastics, 593, p. 424, November 2005
- E Cañibano and others, implementation of pultruidos profiles in the manufacture of refrigerating boxes. Modern plastics, 585, p. 262, March 2005
- JEC 2004, plastics Modernos, 577, page 14, July 2004
- Analysis of wind energy, energy Tecno, 51, p. 26, June 2006
- The chemical and its public perception, 560, Q and I, page 14, September, 2005
- Chemistry and sustainable development, Q and I, 564, p. 18, May 2006
- The chemical must be given priority in the programme VII framework, Q and R, 565, p.
Paper presented at the Conference on composite materials 18as / plastics reinforced organized by the Centre Spanish of plastics