Containers in contact with foods
15 June 2012
The destined containers to this use, as well as the installations where manufacture have to fulfil with some minimum requirements of hygiene and hygiene, to ensure that they can not contaminate and in this way neither the foods that contain.
In the present article review those requirements that are of forced fulfillment for the companies that manufacture alimentary container and those that of voluntary form can help to the companies to improve the quality of his products, increasing his competitiveness and ensuring the inocuidad of his containers. For this recopilan those prerrequisitos basic inside these Systems of Management and stands out the importance of the control of the trazabilidad, different methods to achieve it.

Compulsory legal requirements
The compulsory minimum requirements are the have the company of the industrial sanitary ware register (RSI) as the established in the Royal decree 191/2011 (BOE, 2011), and the realisation of the corresponding essays of migration (so much global determination as specific) of the products finished, such as it determines in the Regulation (CE) Number 1935/2004 (OJEU, 2004).
Systems of management
In addition to these compulsory requirements, are to disposal of the companies other normative requirements volunteers that serve to increase the competitiveness of this type of companies and open way to new markets. Between them we find the following:
- System of Management according to the norm of quality JOINS-IN ISO 9001:2008 (Aenor, 2008), including for the requirement 'Environingingment of work' the development of a System of Analysis of Dangers and Critical Checkpoints (APPCC).
- System of Management for alimentary container according to the norm of quality and alimentary hygiene JOIN-IN ISO 15593 (Aenor, 2008), specific for these products.
- System of Management for alimentary container according to the English alimentary protocol BRC/IoP (BRC/2011).
- System of Management according to the norm JOINS- IN ISO 22000, standard designed to cover all the processes carried out in all the chain of supply that affect so much direct as indirectly to the products that consume , including of this way from the transformers of container until the final distribution of the product (Aenor, 2005).
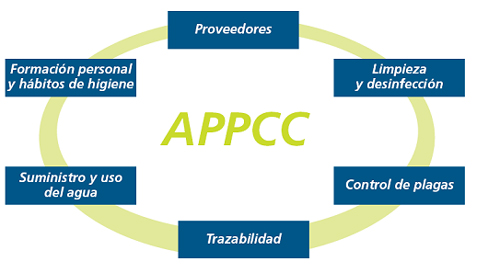
All these Systems of Management of the Quality and Inocuidad of the container have in common the establishment of a series of prerrequisitos to ensure the inocuidad of the same by means of the control of the hygiene of the installations and the personnel of the company. These prerrequisitos are:
- Have by part of the company of a complete definition of the products object of the scope of the system of management.
- Have of a complete definition of the productive process, to know that way and by that productive phases raisin the product and facilitate in this way the identification of possible points of pollution of the product.
- Carry out a control of the water used in the different productive processes to ensure his potabilidad and in this way ensure that in front of any escape of water would not contaminate the container.
- Have implanted and registered a Plan of cleaning and hygiene to have of some conditions of optimum hygiene for the manufacture of these products diminishing in this way the possibilities of pollution by dirt and microorganisms a container.
- Carry out and register a control of plagues, to avoid the pollution of the products by insects, rodents, etc.
- Control the specifications and the alimentary aptitude of the raw materials, packaging, labelled, cleaning products and chemical products used in the manufacture of the containers and/or in the maintenance of the equipment and installations.
- Evaluate to the providers of raw materials, essays, etc. to ensure us the idoneidad of the raw materials, etc.
- Endow of relative suitable learning to the best practices of manufacture to the workers, to avoid the pollution of the containers by a bad manipulation.
- Control the trazabilidad of the products to be able, in case to have some incidence with some product, to be able to withdraw of the market the products affected and be able to detect with that material/is has manufactured and/or to which customer/is has served .
- Definition and control of the flows of traffic for the personnel and the different materials inside the installations, so that they avoid possible 'pollutions crossed'.
A prerrequisito in which detain by his importance in alimentary hygiene and complexity in some cases, for his control, is the trazabilidad. For the concrete case of the containers for food that commercialise empty, is less critical that in the case of the distribution of the container with the food in his interior (e.g., the precooked products), but equally applicable.
Usually the control of the trazabilidad establishes by means of control of batches. This method allows to know all the phases by which has happened the product, raw materials employees and location.

In the year 2011 publishes the European Regulation 1169/2011 (OJEU, 2011) that will not go in in force until the year 2014. Of this directive gives off the obligation to have of additional information of the food (content in the container), in databases and impresa in his labels in shape of table (content in possible alérgenos, place of origin, the quantity of fats, carbohydrates, glucides, proteins, dates, number of batches, etc.). This fact shows that every time the consumers have the need to be more informed on the products that consume by what will be necessary new supports to transmit this information to avoid collapse of messages the containers.
In the actuality, the technology endows us every time of a greater quantity of resources as it is the case of the bar codes, the systems of identification by radiofrecuencia, known like labels RFID and the codes QR. These systems are especially interesting for the companies that manufacture and distribute a food packed. We can define in brief these technologies eat:
- The bar code, consists in a system of labelled represented by a series of parallel bars and spaces where stores information of text encoded, this information can read through an optical device.
- The labels RFID, consists in an automatic system of identification, similar to a sticker, chip that contains a receptor that allows him receive and answer to signals of radiofrecuencia by means of a reader.
- The codes QR or Quick Response Barcode, is a system to store information in a matrix of points or a two-dimensional bar code. They have a square geometry and present three square characteristic in the corners that allow to detect the position of the code to the reader.
The bar codes and the RFID, like methods more used by the companies in the actuality differentiate basically in the following appearances:
- In the case of the bar codes the main advantage is his economic cost, but has a series of limitations like that only it is possible the reading of an only code every time and needs for the reading that the code was visible directly, the capacity and storage is low since they identify by type of products, spoil easily, are of an only use, no can him integrate sensors.
- The labels RFID have the inconvenient that his cost is high, can carry out a simultaneous reading of several products since it does not require visual contact of the reader with the label, fact that allows a big capacity of storage, are more resistant that the bar codes and exist some types that are reprogramables being able to integrate sensors.
- The codes QR, are the newest system, that still finds in expansion, in his starts has used to follow the trazabilidad of products but at present is turning into a powerful tool of marketing for the companies. It has the advantage to allow contain big quantity of information and the accessibility by the final consumers through the readers of telephony that have developed .
Conclusions
The companies involved in the alimentary chain find inside a sector where the hygiene of the final consumer is elementary, being prioritario for the companies ensure the quality and inocuidad of his products. For this end, the companies have increasingly, of a big quantity of norms to facilitate them this work.
Shows of the importance of the hygiene required in this sector is the development of constant of new technological applications to control key appearances as it is the one of the trazabilidad.
Aiju Has of qualified personnel to carry out the advice in the implantation of a big variety of systems of management for this and other sectors, as well as of a laboratory to carry out the essays of migration of products to be in contacts with foods (for example, containers or biberones).
References
Aenor (Spanish Association of Normalisation and Certification), 2005. It JOINS- IN ISO 22000. Systems of the inocuidad of the foods. Requirements for any organisation in the alimentary chain. Aenor, Madrid.
Aenor (Spanish association of Normalisation and Certification), 2008. It JOINS- IN 15593. Containers and packagings. Management of the hygiene in the production of the containers for alimentary products. Aenor, Madrid.
Aenor (Spanish association of Normalisation and Certification), 2008. It JOINS- IN ISO 9001. Systems of management of the quality. Requirements. Aenor, Madrid.
BOE (Official Bulletin of the State), 2011. Royal decree 191/2011, of 18 February, on Sanitary ware General Register of Alimentary Companies and Foods. BOE, 57 of 18 February, Madrid.
BRC (British Retail Consortium), 2011. Global standard for packaging materials, Issue 4. BRC, London.
OJEU (Official Journal of the European Union), 2011. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 OF THE European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the alimentary information facilitated to the consumer and by which modify the Regulations (CE) number 1924/2006 and (CE) number 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and by which derogate the Directive 87/250/CEE of the Commission, the Directive 90/496/CEE of the Council, the Directive 1999/10/CE of the Commission, the Directive 2000/13/CE of the European Parliament and of the Council, the Directives 2002/67/CE, and 2008/5/CE of the Commission, and the Regulation (CE) number 608/2004 of the Commission. OJEU L304/18 of 22 November 2011.
OJEU (Official Journal of the European Union), 2004 Regulation (CE) Number 1935/2004 OF THE European Parliament and of the Council of 27 October 2004 on the materials and destined objects to go in in contact with foods and by which derogate the Directives 80/590/CEE and 89/109/CEE. OJEU L338/4 of 13 November 2004.


































