This news article was originally written in Spanish. It has been automatically translated for your convenience. Reasonable efforts have been made to provide an accurate translation, however, no automated translation is perfect nor is it intended to replace a human translator. The original article in Spanish can be viewed at
Ejemplos de aplicación del Mecanizado de Alta Velocidad (2ª parte)Examples of application of the high-speed machining (part 2)
Juan Martín - Technical Commercial - Juan Martín, S.L.
15/03/2002MACHINING OF MOULDS AND DIES
The moulds and matrices are, without doubt, the most comprehensive implementation of the new philosophy of high speed machining. In this sector, the introduction of this new technology means more than buying a new machine tool.
In general need to oversize technical offices because as already explained in the chapter 6, the time required for the CAM is clearly superior to the need for more conventional cutting strategies.
Instead section of EDM will be reduced for sure, because as also mentioned, you can now machine to boot material chips which were previously unthinkable thanks to new coatings of tools, and also more complex forms with smaller radios due to the stability of the new heads can be played and the precision and dynamics of drive system.
For this reason is always uncertain of manual polishing times minimize and can almost eliminate the processes of final adjustment (thanks to the precision of the machine and the non - vagueness of the human hand).
All together allows you to reduce delivery times and improve the quality, which is the real objective of the machining of high speed in this sector.
Spain, and in particular Catalonia. One of the European regions with a high moldesy density is matrices and this industry is undoubtedly the first field of application of machining swarf removal.
Each of the sectors of the pier and matrices faces, but various problems and high speed machining can also respond in various ways to these needs. The following is a study particularized with any of these sectors.
Plastic injection moulds
This is the wider sector of the molds. Component of all types of plastics are manifold and are present at all levels of our lives. If in any environment we look at the number of objects made of plastic, and is thought that each of these objects can speak one or various plastic injection molds, may have an idea of the power of the sector.
In Catalonia are manufactured moulds for injection of plastic for wide range of activities but we could be noted in the automotive sector, in which much of the production is exported to major European areas of automotive manufacturing / including Spain).
The characteristics of the mould of injection of plastics are so diverse like the same components, thing that does difficult to argue global solutions for all the companies of the sector. The precisions, the superficial finishings, etc. are very different between a destined mould to the manufacture of telephone connectors or medical equipment and another destined to bumpers of car.
Now, the sector feels the constant pressure of shorter delivery deadlines and quality requirements that 5 years ago were unthinkable ever.
Globalization, is also opening up all markets in the world, and therefore the competence of the mould industries are often in less developed countries where the fixed and labour costs are lower. Processors are still placed nearby, for example, of car manufacturers because the additional cost of transport is too expensive per piece. But for a mold that injects millions of pieces, and with the current means that ensure the quality, the distances are not any impediment and factors of choice of suppliers are no longer geographic, but of, and in this order, terms of delivery, quality and price.
Nothing more than technological innovation can, therefore, maintain assessments of the market for this industry in our country. High speed machining, is one of the means to resolve these conflicts, with the following strategies:
- Specialisation of the industry. To the technology of mechanised of high speed the dimensions, precisions and characteristic of the materials are very important, and dominate this technology for any type of mould does , almost always unfeasible. It requires , therefore, specialisation in a type and dimension of mould that forces often to exceed borders if it wants to increase the production (globalisation). This realisation involves also the outsourcing of auxiliary works, that at the same time will be specialisations of other companies of the sector (for example, the manufacture of carry-moulds and other normalised).
- Adoption of methods of automatic manufacture without presence of operators. The labour costs will be always lower in other parts of the world and has to try reduce them. The machines of high speed are more expensive but, in general, much more thought for the automatic operation. To other the strategies of mechanised of high speed try already do constant the conditions of cut, avoiding like this break of tools.
- Redesign of the stages of the manufacture simplifying them and doing easier his planning and control. The reduction of the processes of spark-erosion, whenever they are possible, are fundamental for the saving of time in the same time of spark-erosion and in the one of manufacture of electrodes of copper or graphite, that do not contribute profit to the mould. The only elements that still continued being property of the spark-erosion are the corners with radios very resembled 0 and the very deep slots (think that with mechanised of high speed arrive to do slots with esbeltez depth / width = 15.
- Also in a lot of cases, reduction of the times of manufacture by the possibility to mechanise directly the blocks of temperate steel from the desbaste until the finishing and save like this the thermal sensors treatments intervals. These processes are always subjects to condicionamientos economic, but if they consider all the factors involved is often very advantageous.
- The rapidity of the processes of high speed allow to do happened of mechanised much smaller improving in 4 or 5 times the superficial finishings with a time of mechanised alike or slightly greater, Like this allows to reduce the manual processes of polishing, saving hand of work very expensive. The mechanised of high speed can arrive to produce acabamientos superficial of Ra = 0,1 mm and better, surpassing limit them of the erosions in time considerably better and without need of production of electrodes.
- The static and dynamic precision of the new machines of high speed, and the minimum presence of manual operations allow many times delete the processes of adjust of moulds, that often last weeks and suppose very high costs in money and time.
But these advances are not here. The increasingly important presence of the moldistas in the phase of design of automobile components, can allow the adoption of new forms of product that make easier the implementation of high speed machining and therefore to reduce overall costs to the sector.
Below are some examples of machining using the technology of high-speed (figures 14, 15, 16).
Fig. 14.- Male of a mould of injection of plastic for
tapacubos. Piece of Ø470 in steel pretratado to 46 HRc.
Total time of mechanised from the desbaste to the finishing: 17 h.
Fig. 15.- Whole mould (male and female) of the carcasa
outside of a telephone of table. Until the slots of the male
are mechanised in the centre of mechanised.
All the surfaces are finished of machine, without pulir.
Material DIN 1.2344 to 54 HRc.
Total time of mechanised 28 hours for the female and 52 for the male.
Fig. 16.- Female of a tiny mould for the
manufacture of one covers of batteries.
Temperate steel to 54 HRc. The biggest tool used is of Ø0,5 mm and the smallest Ø0,2 mm.
Time of mechanised 1,5 hours.
Aluminum injection moulds
The requirements of the product in this sector are very similar to the moulding of plastic injection and also, therefore the benefits of high speed machining.
But they have to point out some characteristics:
- The components of aluminium uses often in applications where needs an efficient refrigeration and include therefore aletas of refrigeration. These, in the moulds, Suppose slots very slim that traditionally have supposed big productions of electrodes of graphite and dedication in time to the processes of spark-erosion. This element has to be therefore one of the aims of the mechanised of high speed in this industry (figure 17).
- The superficial finishings are not so critical as in the case of the mould of injection of plastics when being, in general, the components of aluminium functional pieces no seen. To other the same injection of aluminium does not achieve superficial qualities to the very good pieces. If they need components seen of aluminium often finish in processes of automatic polishing.
Fig. 17.- Cárter Of the engine a motorcycle. The slots
that conform the aletas of refrigeration are very deep.
Material DIN 1.2344, 54 HRc. Time: 9,5 hours
Blow moulds
Blow molds are a different case in the mold of plastic components. These molds are used for the manufacture of plastic bottles. The highest consumer sector is above all mineral water and refreshing drinks.
The operation of the mould is not injection. Used a preform of injected plastic (this component is really pumped and requires very high precision), which includes the thread container lengthened with a certain thickness of walls. This preforms lies inside the mould and blowing hot air on the inside of the preform that heats plastic and makes it to expand against the walls of the mold. This gives the mold particular characteristics:
- The mould manufactures in aluminium because to the not existing a lot of rozamiento of the plastic can achieve productions quite high. The machines devoted to these moulds have to have suitable characteristics for these materials. The mechanised of the mould supposes a very limited time.
- The superficial finishings are very demanding. At all more it is necessary to check the surfaces of the bottles of plastic. The mechanised of high speed can save time of polishing that is porcentualmente, very elevated in these types of moulds. In this sector began , does years, to use interpolations NURBS to recess time and improve the superficial quality.
- The production of a determinate component (for example the bottle of 1,5l of Font Vella) is very intense (some cientos of thousands or millions each day) and therefore they have to manufacture a lot of equal moulds. This allows to reduce the costs of programming by mould, and optimise the paths to try improve time and superficial finishings. Very often they can use machines of mechanised horizontals more common in the fields of production of final piece, taking advantage of it better evacuation of the shavings that present these configurations, and the auxiliary elements to reduce the time of no cut like cambiadores automatic of pallets. In a palet can mount a cube and in each one of his sides a mould improving the autonomy of the machine and doing the most economic process.
- Traditionally these moulds have not used never in spark-erosion, and therefore, does not give this replacement of technologies.
Figure 18 shows one of these molds.
Fig. 18.- Mould of blown in material of aluminium.
Time of mechanised 56min. Rugosidad superficial: 0,6 µm.
In hot and cold forging matrix
This sector also requires parts repeated, thus reducing the cost of CAM by manufactured piece.
The materials used in hot forging are temperate steels (usually DIN 1.2344 of 44-54 HRc). In the chapter 10 has become the economic feasibility study for a company manufacturer of this type of arrays. Other features of the sector are explained in the feasibility study.
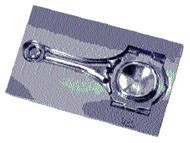
Figure 19 shows one of the most studied matrices of hot forging.
Fig. 19.- Matrix of forge hot for the production of
bielas for the sector of the car. The material is welding of
very low maquinabilidad. Total time: 2 hours
Cold forging uses materials even more hard and difficult to machine (such as for example a material of the company Uddeholm, ASP-23, arriving after the heat treatment to 62 HRc).
This sector is debated still between whether or not to adopt high-speed machines, or continue with EDM machines. As it has been explained in the chapter 5, dedicated to the tools, the performance of these much low hardness 62 HRc, so costs can be unviable.
As well, and the future is clear, nothing more than a small step of tools can unseat the electroerosiones completely. There already, in every way, are companies using high-speed machining to produce their arrays of wrought iron cold.
Figure 20 shows the punch of a matrix of cold forging for the manufacture of homocinéticas colzas for the direction of the car.
Fig. 20.- Punzón For the manufacture of rapes homocinéticas.
Material: ASP-23. Hardness: 62 HRc. Time: 3 hours
Arrays of extruded aluminium
The matrices of extrusion of aluminium use in presses of extrusion that conform the aluminium in profiles. These use basically in the construction (doors, windows, etc.).
This sector also requires large productions of parent but in this case not repetitive. Anyway the arrays of extrusion have elements morphologically very similar and the changing element is the profile of calibration which is only made with wire EDM.
The materials used are also DIN 1.2344 technical treatments to induce them to 52-54 HRc (Figure 21).
Fig. 21.- Piece bridge of a matrix of extrusion of aluminium.
Material Din 1.2344 to 54 HRc. Total time of mechanised: 2,5 hours.
The advantages of production and high speed machining are clear for this sector.
The main problem of these matrices is the delivery time. They are trying to reduce below a week.!! Traditionally the roughing occurs with the still soft material, is tuning, and then just in the Centre of machining and wire EDM. So many of these companies incorporate heat treatment facilities to reduce time.
Yet this time to tighten up one of these matrices is never less than 24 hours, which is 20% of the total time of production of the matrix.
High speed machining is beginning to revolutionize the industry. Leading companies have already adopted this new technology by simplifying the process of machining integrated into machining center from the block already tempered, saving changes of machine operators, time and costs.
In a very short time the substitution of penetration EDM is almost 100% in this sector.
The total process is then simplified in machining in high speed machining and wire EDM Center to form the calibration of the profile.
CENTRE OF MACHINING FOR MOULDS AND MATRICES OF PRECISION
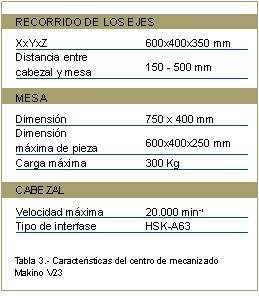
For this application we have chosen the Makino V33 machining of Japanese Manufacturing Center. Below is the image and fundamental characteristics of the machine (Figure 22 and table 23, respectively).
It's a centre of high speed machining designed to manufacture parts of ultra precision with excellent surface finishes. It is therefore suitable for moldistas of injection of small parts (moulds multicavidad).
We will then see the technical solutions that have been developed for this model, and how these features has been made.
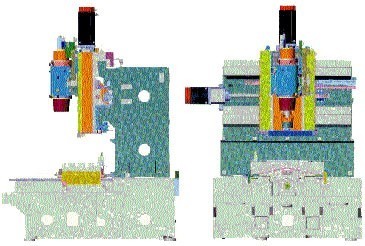
Fig. 22.- Appearance of the centre of Makino model V23
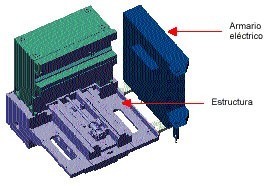
Fig. 23.- Structure of the machine Makino V23
Fig. 24.- Diagram of the structure of the machine Makino V23
Structure
The structure of the machine is designed to improve the static and dynamic accuracy of conventional schools. Very extensive hydrodynamic guides are used to increase the damping of vibrations and thus improve surface finishes (figures 23 and 24).
Increasing the rigidities of the cars on the X and Z axes with distances between very extensive guides and lengthening the z-axis guides avoiding overhangs, as well is the rigidity of the system in any position of the axes.
The ball spindles are also extra - rigid. The diameter of 45 mm and 8 mm step you make up a very high response to the needs of acceleration for the realization of complex 3D paths.
CNC and drive systems
Systems of measurement of the drives incorporate encoders and rules.
The encoders are the closing of the loop speed. These have resolution of 1,000,000 pulses per lap.
The TNC of this machine uses the basic technology of the FANUC 16iM but the control of the axes is programmed by the manufacturer of the machine adapted well to algorithms equations of response of the mechanics of the machine.
The kinematics of the axis chain, new systems of measurement of high resolution and algorithms of numerical control adapted to the mechanics of the axes allow us to obtain details and exceptional surface finishes.
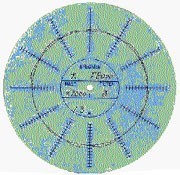
The accuracy is checked mecanizing a circle of Ø40 mm in aluminium to 8000 mm/min in advance. Results are presented in Figure 26.
Fig. 26.- The proof is to show an error of circularidad
maximum of 1.3 µm, in an advance of 8.000 mm/min.
The 0.1 µm can be controlled with this new system of reading of the position.
This greatly improves the surface finish of the parts.
In figures 27 and 28 are shown, a microscope, the differences between a finish with the loop of standard 1 µm position and the other with the Lasso of position of 0.1 µm. The 27 shows the finish with feedback of 0,001 mm and the 28 of feedback of 0,0001 mm
Fig. 27.- Finished with feedback of 0,001 mm
Fig. 28.- Finished with feedback of 0,0001 mm
Head
The head of the machine is one of the most special on this machine elements.
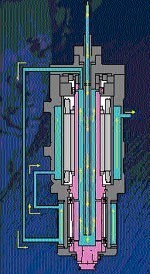
To get pieces of ultra precision is needed that the head also keep details below 0.002 mm. The thermal control of this must be, therefore very rushed. Your cooling system is shown in Figure 29.
It's a head integrated with double winding engine to achieve respectable couples at low revolutions. Maximum revolutions are 20,000 rpm.
Fig. 29. The head cooling system
As it has been explained in the chapter 8, the dichotomy between power and speed of head occurs fundamentally impossible with normal cooling systems, mounting bearings (large size) on a head of high speed and with a very acceptable estimated life.
The head of the machining center presents two characteristics which allow to exceed the values set out in the chapter 8.
- direct Refrigeration of the rotor. The cabezal (as it sees in the figure 28) refrigerates first inside the rotor, afterwards cools the outside of the frontal threads and finally the devaneos of the stator of the engine. This refrigeration is very efficient because it evacuates the heat directly of the place where concentrates the greater number of focus: the stator. To other this refrigeration controls to act with more intensity when it increases the speed of the cabezal, Like this, to more speed, the rotor of the cabezal is colder that the fixed part and therefore it lightens the precarga of the threads. This allows us precargar the threads to low revolutions, obtaining like this a cabezal able of an axial and radial rigidity very high in the revolutions where do the desbastes. And instead to other revolutions when the efforts of cut are minimum to free the precargas.
- Lubricación direct of the internal cage of the threads. The same oil that uses for the refrigeration of the interior of the rotor, lubricates directly the inner cage of the frontal threads, by means of some holes that practise before the setting. This lubricación allows us figures DN 5 upper times to the obtained with refrigeration air- oil. Have therefore more game with the size of the rolling (in the machine mount threads of Ø interior = 65 mm), and the effective life of the same lengthens (20.000 minimum hours).
This header exceeds in all respects to the heads of similar machines. The surface finishes that are obtained with the machine are also much higher (up to Ra = 0.03 mm, i.e. the mirror).
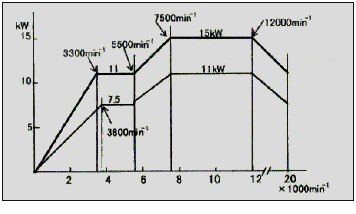
The figure 30 sample the charts of power and pair with regard to the speed of the cabezal.
Fig. 30.- Graphic of power and pair with regard to the speed of the cabezal.
Auxiliary systems
This machine specially designed for the machining of ultra precision parts and excellent surface finishes for molds.
These pieces are usually small and therefore the amount of material to be machined is insignificant. Therefore the machine not incorporated, at least in series, no chips extractor.
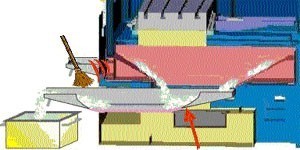
These can be with the hand while this machine in operation with the intelligent system described in Figure 31.
Fig. 31.- extraction equipment equipment equipment of shavings by means of a drawer that can vaciar while the machine finds in operation.
Thermal control and evacuation of heat
To obtain inferior precisions to the 0,002 mm are necessary controes thermal sensors strict that prevent the contribution of heat to the structure.
The motors of the axles have ventilation forced to extract the heat generated in his reeled and threads.
The unions engine-structure and the cabezal of the machine refrigerate and keep to +-0,5oC of the temperature of the structure. This temperature is controlled by thermal sensors sensors that do of input to the system of realimentación of the refrigerador.
The emulsion refrigerante also refrigerates to +-0,5oC of the temperature of the structure.
The sources of heat, such as the electrical cupboard, keep always with a thermal sensors barrier not to contribute heat to the structure (figure 32).
Fig. 32.- thermal sensors sensors barrier between electrical cupboard and structure
5) METALUNIVERS March 2002
Related Companies or Entities