The extent of the potential of oxygen in the process of heat treatment of metals
December 1, 2008
The diagram of Figure 1 shows this feature for various elements. Nickel for example, body to become NiO in an atmosphere with a potential top - 60 kcal/mol to 1000 ° C or - 81 kcal/mol at 500 ° C. Chromium has a greater affinity with the oxygen that nickel as indicated by the bottom line of the diagram. It would require a potential of oxygen less than 130 kcal/mol to 1000 ° C to avoid oxidation. Therefore, a right atmosphere to prevent oxidation of the nickel would not obstruct the oxidation of chromium. The lines of the diagram are for oxidation state lower element.
This type of diagrams allow to determine the theoretical level of the potential of oxygen for a variety of conditions. For example, if you want to decarburar the steel through the oxidation of part of the carbon in the metal, but at the same time you want to prevent the oxidation of the metal to 1000 ° C, it could be achieved with a potential of - 100 kcal/mol oxygen. Below 750 ° C, it would not be possible to decarburar without oxidize the iron of the steel while the carbon line crosses the line of iron in the diagram of the free energy at this temperature.
In the past, the measure of the ability of oxidation/reduction in a protective atmosphere, or the potential of carbon from a fuel atmosphere, was achieved by deduction either by measuring the content of CO2, either using the CO/CO2 ratio either through the point of rocío (moisture content), depending on the nature of the atmosphere. However, these measures can be related directly to the potential of oxygen or to the partial pressure of oxygen. For example, a rich exothermic gas with a ratio of CO/CO2 of 10 has a potential of - 93 kcal/mol oxygen or a partial oxygen pressure of 10-16 atmospheres at 1000 ° C. On the other hand, an exothermic gas with a ratio of CO/CO2 of 0.1 has a potential of - 70 kcal/mol oxygen or a partial oxygen pressure of 10-12 atmospheres at 1000 ° C. Cracked ammonia, which is often used for the temple of stainless steel, is monitored by the extent of the dew point. This is related to the content of water in the gas which is extracted from the H ratio2/h2or (assuming that the content of H2 is known and constant) which in turn relates to the potential of oxygen.
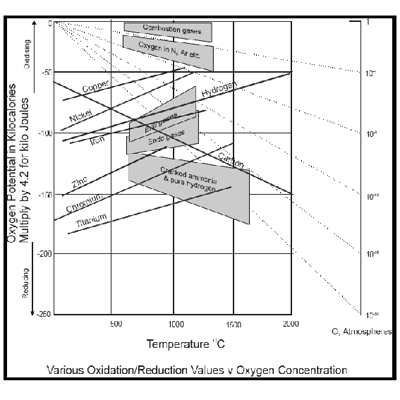
These data only provide information about whether a metal body under certain conditions; It says nothing about the rate of oxidation, etc. Factors such as these will mean that they can afford high oxygen potential of those theoretical considerations alone would indicate. In addition, in some cases, some oxidation of the surface of the metal may be acceptable. Factors such as these in determining the most cost-effective manner of carrying out a process should be taken into consideration. A cell of zirconia oxygen Analyzer can provide valuable information to analyze the effect of various conditions, as well as controlling the optimal condition once it has been established.
Atmospheres
Exothermic atmospheres occur with the burning of a gaseous fuel, typically natural gas or methane, in varying amounts of air. These atmospheres can vary widely depending on the composition of the air/gas ratio. You are commonly called atmospheres rich or poor. The rich atmospheres contain too much fuel that sometimes supposed to be flammable themselves, while that poor atmospheres not. The atmosphere is used to protect metals from oxidation during thermal treatment as the temple. The rich atmospheres tend to be used with ferrous metals that require an oxygen content lower than the non-ferrous metals, which tend to use poor atmospheres to protect them.
Exothermic atmospheres are sometimes treated to withdraw water and/or carbon dioxide. Once again, these vary in composition according to the initial gas and the treatment that is performed. They often contain large quantities of hydrogen that can be used as a measure of the quality of the gas along with the potential of oxygen.

Cracked ammonia is produced with the decomposition of ammonia (NH3) into hydrogen and nitrogen. It is a practical way to produce hydrogen and the process can be controlled by measuring the content of hydrogen. Sometimes requires the value 'percentage of dissociation' Hitech K1550 Analyzer can provide.
The burnt ammonia is produced simply by doing this, burning ammonia, usually in the presence of a catalyst. Generates an atmosphere of hydrogen, nitrogen, and water, and is often a little dried by evaporation of the ammonia for cooling the gas. Once again, the monitoring of the content of hydrogen is very important.
Processes that use these gases are mainly of three types:
Annealing: when a metal is heated to soften it before performing other processes such as rolled or formed. According to the atmosphere, it will be useful to monitor the oxygen, hydrogen, or both.
Motor fuel: when you react with carbon-ferrous surface to create an outer layer of harder metal. Today for this application it is customary to use a tube of oxygen in situ. The disadvantage of using a 'exsitu' system would be that soot would be produced in very rich atmospheres. Exsitu of low-cost system can be used in processes of long cycle atmospheres in which is not usually produce much soot.
Cosmetic surface treatment: processes such as the blue and the bright annealing of steel. The blue is often performed in humid atmospheres (indeed occasionally used steam) for what will be necessary to isolate either the sensor to prevent condensation. Hitech Z1900 Analyzer is ideal for this kind of process.
Conversion factors:
(1) Kilo Joule (kJ) = 4.187 x kilocaloría (kcal)
(2) * kJ = (17.6 x log % oxygen) - 34.72
* Only applicable to analyzers of oxygen of Hitech operating 45mV by decade (634 ° C).












































































