Additive manufacture: present and future of the implants biomédicos
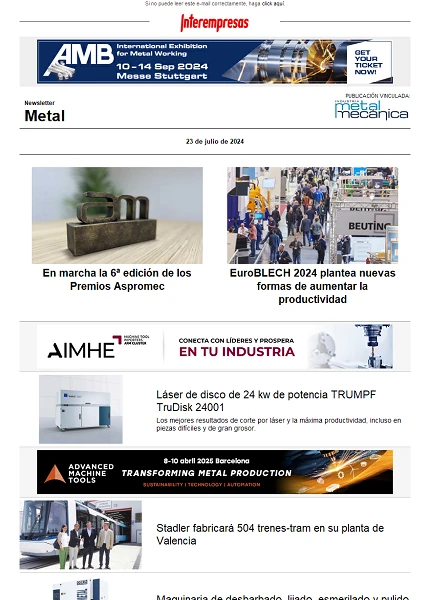
Technical characterisation
One of the most complete definitions of Additive Manufacture is the one who established the Committee F42 of the ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials). According to the ASTM F2792-12to ‘Standard Terminology for Additive Manufacturing Technologies', the Additive Manufacture has been defined like “process of union of materials to create objects, from the information contained in a model 3D, usually layer by layer, by comparison to technologies of manufacture by subtraction, as it is the mechanised traditional” (ASTM, 2010).
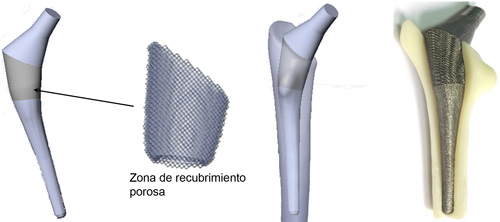
The additive manufacture of an implant initiates with the segmentation of the model 3D of the same in layers very fine (of 30 to 100 µm, according to the technology). The file that contains the information of the group of layers (with the extension.SLI, .SLC, .ABF; According to the technology patented) is envoy to the system of additive manufacture, that reconstructs layer by layer the physical model of the piece in the material wished. Said reconstruction consists in the deposition of a fine layer of metallic dust and the application of a source of power (generally do of laser or do of electrons) on her. The deposition of the first layer realises on a plate of manufacture and afterwards layer on layer. The no reached material by the do remains intact and can recycle for the following manufacture. The result of the manufacture is an identical physical piece to the model 3D of the implant. If necessary, the piece can subject to postprocesado mechanical (mechanised of surfaces of assembling, polishing, etc.) and thermal sensors (homogenisation, HIP, etc.).
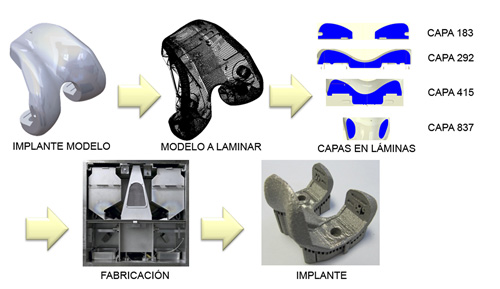
The flow of work in the manufacture of implants by means of FA consists in: design of the implant or in his case reconstruction according to images CT, preprocesado virtual (creation of the archive capeado), digital direct manufacture of the implant, postprocesado mechanical and thermal sensors (if it results necessary), postprocesado sanitary ware (sterilisation, packaging, etc.) and surgical implantation like final step.
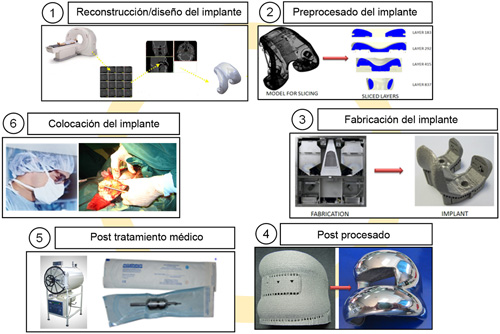
Even being a flow of similar work to the gone on down conventional technologies (forges, the mechanised, etc.), the manufacture of implants by means of FA has important advantages in the production of the implants customizados:
- Reduction of the time of delivery, because of high productivity and direct manufacture of the electronic model;
- High capacity of customización with flexibility of total design, including custom-made porous zones, internal channels, etc;
- substantial Saving in material, because of the recycled complete of the no processed material;
- Absence of toolings and moulds, because of the direct manufacture of the product;
- identical mechanical Provision to the material colado or forged, because of a complete local fusion of dust.
At the same time, the FA has a singular characteristic very valued in the manufacture of personalised products of all type. The camera of manufacture has a middle-sized volume of 250x 250x 250 mm. Like general rule, all the models that can fit in the volume of the camera of manufacture, are manufactured at the same time, since the machine does not interpret models but the layers housed in the archive capeado. Therefore, unlike other processes of manufacture, where each personalised implant is manufactured individually, by means of the FA can manufacture at the same time multiple implants, entirely distinct and customised according to the concrete patient. In the Figure 4 shows a conjoint manufacture of 21 plates of osteosíntesis of fisionomía different. Can manufacture at the same time implants entirely customised reduces costs of manufacture of way very significant and improves the competitiveness of the price offered.
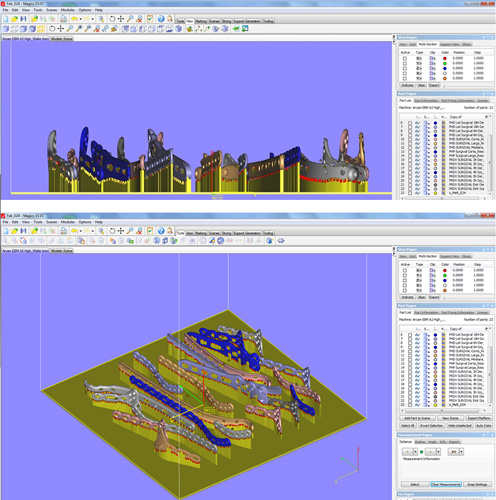
Like this then , results evident that the Additive Manufacture is a very competitive option to the hour to manufacture series relatively short of implants, with high added value and high level of personalización. However, it does not be necessary to forget that with this type of technologies does not pretend substitute the conventional technologies, since the FA can not compete in the manufacture of big series of implants standardised in sizes. However, the development of new materials, the technological improvement, the increase of productivity and the cheapening of equipment around the Additive Manufacture, are realities that go observing year after year, by what seems logical to consider that these technologies can represent the future, no only of the production of medical implants, but of other a lot of sanitary ware products.
Petrovic V et al. (2011). To study of mechanical and biological behavior of porous You6To the4V fabricated on EBM. Innovative Developments in Virtual and Physical Prototyping – Proceedings of VRAP 2011, 28 Sep – 01 Oct, Leiría, Portugal.
Thomsen P. Et al. (2009). Electron beam-melted, free-form fabricated titanium alloy implants: Material surface characterization and early bone response in rabbits, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials Vol 90B, Iss 1, pg 35–44 (2009).