New proposals for the mechanised ecological of components of aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing titanium
Ainhoa Gorrotxategi, division of Industry and Transport of Tecnalia; Ester Sweeps, of Aciturri aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing, and Andrés Bustillo, department of Civil Engineering of the University of Boroughs
04/09/2013The titanium and his alloys are, nowadays and in the near future, material key in the aerospace industry. The improvement of the productivity in the mechanised of these materials is, therefore, an industrial request of prime importance. This article presents a study that shows that, in economic and environingingmental terms, the use of MQL supposes an improvement in the mechanised of these materials, as it reduces the consumption of total power and the consumption of tool by unit of piece manufactured under conditions of usual cutting in the industry, fact that usually questions when it employs MQL. For conditions of cut of very high productivity, the refrigeration by means of liquid nitrogen seem to be an option with an interesting future.
A big resistance in relation with his weight, his properties anticorrosivas and his thermal sensors and electrical conductivity have converted to the titanium and his alloys in a key material in the aerospace industry. The need of new aeroplanes lighter and efficient has not done but increase the demand of this material, in spite of his price, converting to the aerospace sector in his main consumer. The use of this material in aeroplanes reaches components of very distinct nature: from structural elements of the type outline, cuadernas or herrajes as in components of turbopropulsores, rings and carcasas mainly, or of mechanisms, like the trains of landing (Figures 1 and 2).


Nowadays, the productive process more used to the hour to manufacture this type of pieces is the mechanised, process that on the one hand is complex by the nature of the material and by another costly. In the first place it treats of a process by start of shaving that deletes big part of a material that, already of in case, is expensive. Second, the poor thermal sensors conductivity of the titanium does that it was the tool of cut, and no the component of titanium, the one who absorb the intense heat that produces during the operation of mechanised. This translates in a premature and intense wear of the tool. Associated to this produces a high consumption of liquid refrigerante with the end to evacuate the important heat generated, máxime when the titanium is highly flammable. Finally, the processes of cutting realizar to low speed, what turns them into slow processes where the low module of elasticity of the titanium favours that the piece separate of the tool of cut causing ‘chatter' and problems of tolerance in the case, very common in aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing, of pieces of thin walls.

In some surroundings like the current, in which the complexity of the pieces of titanium for the aerospace sector is each greater day and, where besides the companies need to increase his competitiveness, results critical to develop methods of manufacture more efficient for the components manufactured in this material.
To the margin of the economic analysis, nowadays is necessary to consider the environingingmental impact of any product, application or process, already was by the increasingly demanding demand of the society of respect to the environingingment, or, by the obligation to fulfil new laws more restrictivas. Especially, the elimination of the lubricantes results critical, by what in the countries industrialised are developing strict relative environingingmental laws to the utilisation and recycled of fluids of cut in the industry.
These two needs, improve the productivity of the mechanised of titanium and reduce the ecological impact of this process, do necessary the proposal of new alternatives of mechanised ecological of components manufactured with this material. Inside the European Project EMC2 have carried out the evaluation of new technicians of mechanised that affect to the lubricantes used during this process from the double slope of the economic cost and the environingingmental.
New proposals of mechanised ecological of titanium
The aim of the experimentation realizar is can extract clear conclusions on the use of technicians of alternative refrigeration to the taladrina, commonly used in the process of mechanised of titanium. For this, have analysed the quality of the piece mechanised, the productivity of the process, the consumption of resources and the impact in the environingingment.
The experimentation has realizar on probetas of You6To THE4V, type of titanium more common in aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing also known like titanium of degree 5 or You 6-4, with a chemical composition of 6% of aluminium, 4% of vanadium, and almost all the remainder of titanium. This alloy is something more resistant that the pure titanium having the same rigidity and thermal sensors properties (except the conductivity which is roughly 60% minor that in the pure titanium). They have carried out experimental essays of milling to end of life of tool on probetas, with the criterion of end of life of tool of value of maximum wear in the flank (Vb) of 0,4 mm.
Have compared three different technical of refrigeration: i) Taladrina external, ii) MQL external (Minimun Quantity Lubricant), iii) MQL external combined with liquid nitrogen (N2). It has split of the hypothesis that from the point of view of the refrigeration the operations of desbaste are the most problematic in comparison with the operations of finishing. By a part, the discharge of shaving that obtains is greater by what his evacuation can suppose a problem, and on the other hand the temperature reached during the mechanised is also upper what supposes a greater wear of the tool.
The experimentation has carried out with two tools of desbaste in two different machines, with Dry dish Tools Ø32 mm in the fresadora Ibarmia ZV 25/Or600 situated in Tecnalia, and with dish Sandvik Ø125 mm in the fresadora Versa W manufactured and situated in the plant of manufacture that Nicolás Correa S.A. has in the place of Boroughs. They have used the same parameters of cut for both tools, being the speed of cutting the only variable of the process modified and keeping constant the rest of parameters. Like conditions of cut of reference have used the parameters of cut advised by the supplier of tools that, to his time, have contrasted with the conditions of cutting more productive with the object to stress the possible differences between the distinct technicians of refrigeration. During the execution of the experimentation has used a vatímetro to register the power consumed by the machine. For the supply of MQL, the two machines used have of his own team of MQL, as it can appreciate in the Table 1 where summary the main characteristic of the experimentation realizar.
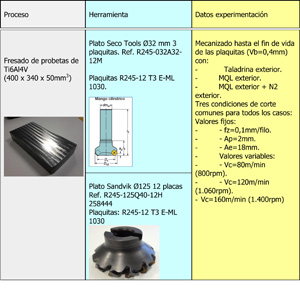
The Table 2 resume the equipment employed during the experimentation.

With the purpose to compare the results obtained with the three technicians of refrigeration experienced (taladrina external, MQL external and MQL external + N2), have measured and analysed the following parameters:
- Length of surface mechanised in function of the wear of the tool.
- Rugosidad Superficial (Rto) of the piece mechanised to analyse the superficial quality of the mechanised.
- Total consumption during the operation of mechanised.
To his time, has realizar an economic analysis and of environingingmental impact generated with each technician of refrigeration.
to) Length of surface mechanised
Measures the length of the shaving mechanised until the end of life of the tool, that is to say, until a wear in the flank (Vb) of 0,4 mm. The Chart 1 sample the value of the length of shaving mechanised that it obtains in function of the speed of cutting and the technician of refrigeration used.
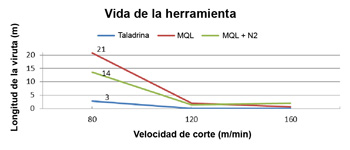
Graphic 1: Length mechanised for the different methods of refrigeration and different speeds of cut for a wear established of Vb=0,4 mm.
Can appreciate that to Vc=80m/min, the length of the surface mechanised is of 21 m when using MQL external, in front of the 14 m obtained when using the combination of MQL external and N2. Instead, when using taladrina conventional, have generated only 3 m of shaving. These data indicate that the wear generated in the tool is greater with the use of taladrina. This is due to that the MQL accesses better that the taladrina to the zone of the tool to cool, increasing his life.
The conditions of cut with Vc suprior to 120m/min are too hard, since, from roughly this limit, the wear increases considerably and the length of shaving mechanised diminish being practically the same in the three cases. The greater length of shaving mechanised obtains with the use of MQL combined with N2 like refrigerante, although the values of 2 m mechanised with MQL+N2 in front of the 0,7 m obtained with alone MQL are quite similar. In the case of the taladrina, has not considered realizar essays to these speeds given the results obtained for a speed of cut of 80 m/min.
b) Analysis of the superficial quality of the mechanised
The superficial quality of the piece is used to to be a fundamental industrial requirement by what also has taken into account in this study. It has measured and compared the rugosidad superficial Rto in the piece mechanised in function of the technician of refrigeration used. The analysis has realizar for Vc=80 m/min, because of his greater life of tool. The Chart 2 sample the average of the values of rugosidad Rto obtained in the different happened of mechanised in function of the technician of refrigeration.
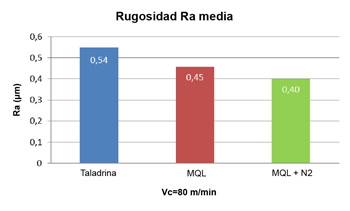
Graphic 2: Average of the values of rugosidad Rto in function of the type of refrigeration for Vc=80 m/min.
Observes that the lower value of rugosidad Rto=0,4 µm obtains with the use of MQL+N2, whereas the worst result of Rto=0,54 µm obtains with the use of taladrina.
c) Total consumption during the operation of mechanised.
To compare the total consumption of the operation in function of the technician of refrigeration used, have taken into account different consumptions generated during the mechanised: the energetic consumption (obtained by by means of vatímetro of the power consumed by the machine during the mechanised), the consumption of oil, the consumption of water and the consumption of nitrogen. For the comparative takes like reference the mechanised with taladrina assigning him a value of 100%, and calculating the corresponding percentage to the others two technicians of refrigeration. In the Chart 3, can observe the comparative of the total consumptions for each one of the appearances studied, in function of the technician of refrigeration used.
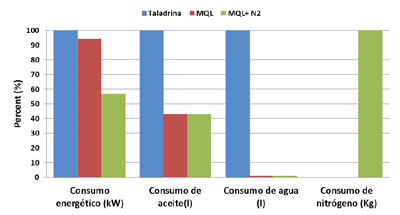
Can observe how in the case of the MQL and of the MQL+N2, the consumptions of power, oil and water are inferior that in the case of the taladrina, but when including the consumption of Nitrogen in the MQL+N2, the main conclusion is that from the point of view of the consumables, the MQL is the most interesting option. In the case of the energetic consumption the main difference is been due to the bomb of taladrina and MQL and in the case of the MQL +N2 is inferior since for the same volume of shaving evacuated, when being the Speed of cutting the double (of 80 to 160 m/min) the time that the bomb is in operation is the half. In the following section, will value economically the different options.
The cost by volume of material mechanised (€/cm³), that depends directly of the discharge of shaving (cm³/min), is a parameter that allows to realizar an economic study of the process of mechanised. It has estimated the discharge of corresponding shaving to the same value of wear of tool of Vb=0,4 mm for each technician of refrigeration (taladrina, MQL external, MQL ext+N2). For each one of the technicians has chosen the speed of cutting more productive for the value of wear mentioned. The Chart 4 sample the values of discharge of shaving with value of wear 0,4 mm for each one of the tools and technical of refrigeration.
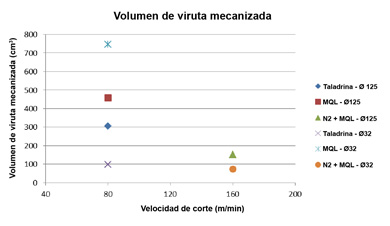
To calculate the cost of the operation of milling have taken into account the different costs of the tool, of the refrigerante (oil, water and Nitrogen) and the consumption of power of the machine. It has taken like reference a piece type of profile in T of titanium of the company Aciturri, whose volume of shaving to delete is of 512 cm3.
The costs of the tool have calculated with the data obtained of the experimentation realizar with the tool of Ø32 mm with three plaquitas, being the cost estimated of each plaquita of 15 €. With these values, obtains the cost of wear of the tool for each technician of refrigeration, taking into account the volume deleted with each one of the technicians to the speed of cutting that has considered more ideal for each technician of refrigeration, Vc=80m/min in the case of the taladrina and of the MQL and Vc=160 m/min in the case of the MQL+N2.
The cost of taladrina calculates from the estimate of consumption of taladrina of a machine of roughly 6.000 litres/year. It considers taladrina with a concentration of oil of 7%, and considering costs of oil and standard water estimated of €2,8/l in the case of the oil and of 0,00068 €/l in the case of the water.
The cost of MQL calculates from data supplied by the manufacturer of the system MQL. In this case, of the system Lubrix 750. The consumption of oil in the level 15 for the strawberry tested is of 35 ml/h (180l/year) to a price estimated of 16 €/l.
The cost of the Nitrogen estimates in €5,57/piece calculated taking into account the time of broadcast of the gas during the time of mechanised.
The cost of the consumption of power bases in data obtained during the experimentation (consumption of the machine in empty and during the process) and data supplied by the manufacturer (data of the pumps of MQL Lubrix 750 and of taladrina).
Have not included the costs of the necessary initial investment for each one of the technicians.
In the Table 3 show the different costs calculated, for each one of the technicians of refrigeration.

Can observe how the mechanised with MQL is the one of lower cost by piece of the three technicians analysed. In the case of the MQL+N2, the by piece obtained cost gives an interesting value comparing it with the taladrina, but it would be necessary to loan special attention to the time of change of plates and think in a time of external manufacturing for the tuned of the upper tools to the others two cases since the volume of shaving evacuated is lower that in the others two cases.
Nowadays has a special environingingmental motivation since of the elimination of the lubricantes results a lower pollution. In the countries industrialised, are evolving strict environingingmental laws surroundings to the utilisation of the fluids of cutting. Thus, it has considered interesting realizar an analysis of the environingingmental impact that supposes each one of the technicians of refrigeration analysed.
Have used the following two ratios to measure the environingingmental half impact, in addition to the previously calculated consumptions.
Management of energetic Efficiency: it determines the percentage of energetic consumption of the process of mechanised with regard to the energetic consumption total.Footprint of Carbon: they calculate the broadcasts of gases of effect invernadero of the operation analysed and of the cycle of life of the products that have taken part during one or another process. In this case they have taken into account the footprint of the oil, of the electricity and of the hard metal of the tools.
In the Table 4 show the values obtained for these indicators in the three cases.

Can observe how the use of MQL is the case of lower percentage of energetic efficiency or, what is the same, where the energetic consumption during to the process of mechanised is lower regarding the total consumption for the three technicians of refrigeration. On the other hand, from the point of view of the footprint of carbon, the case of the MQL +N2 presents a slightly inferior footprint to the others two cases. It is necessary to take into account in this case that the conditions of cut in which it uses MQL +N2 (160m/min) duplicate, for the same wear, the alcanzables with MQL or taladrina, reducing the time of mechanised to the half.
Conclusions
This work has allowed to obtain the following conclusions:
- Is possible to mechanise titanium You6To the4V in operations of desbaste in milling with MQL of productive way, obtaining resulted of rugosidad Rto similar to the obtained with taladrina.
- The final quality of the pieces mechanised does not present substantial differences, neither dimensional neither in the rugosidad superficial, depending on the technical refrigeration of tool chosen.
- The consumption of power results to be a factor diferenciador, had to mainly to the consumption of the bomb of the circuit of taladrina. In the case of the MQL+N2 the consumption results roughly the half that the others two technicians studied, since the speed of cut is the double that in the case of the MQL.
- The price of the tool supposes a very high percentage in relation with the costs of consumption of power and flowed of cut in the total cost of the process of mechanised, by what the life of tool is a key factor to the hour to obtain the relation cost/productivity.
- To consider the option MQL+N2 in operations of high productivity it would be necessary to consider other appearances like the manufacturing of several tools and the fast change of the same in machine, data that have not valued in this study.
In summary, this study shows that, in economic and environingingmental terms, the use of MQL in the mechanised of components of titanium for the aeronautical sector component manufacturing sector component manufacturing industry supposes an improvement in front of refrigerantes traditional, fact that usually questions . This economic advantage is feasible thanks to the identification of some conditions of productive cutting and to the reduction in the consumption of total power during the cycle life that produces the use of MQL. More still, the use of MQL in the mechanised of titanium can suppose a considerable saving in the total cost of this process, given the high percentage that supposes the price of the tool in the total cost of the same.
Gratitudes
This work has been partially funded by the Comision European through the Project of the 7º Program Marco NMP-285363 ‘EMC2-Factory- Echo Manufactured transportation means from Clean and Competitive Factory'.








