How choose a valve of ball to reduce broadcasts
The fugitive broadcasts define of diverse ways and can refer to a wide range of broadcasts that do not limit to chimneys or venteos, but they include pertinent broadcasts of the manipulation and processed of raw materials, dust and other industrial processes.
With regard to the broadcasts in general, and the fugitive broadcasts in particular, the tendency is to regulations more strict and more control. The fugitive broadcasts will be in the avant-garde to measure that the legislators try to impose the next level of norms regulatorias, especially in what it concerns to the volatile organic compounds very reactive (HRVOC).
No all the escapes consider fugitive broadcasts. The escapes can be internal or external. In the case of a valve of ball, an internal escape means an escape through the seat, of waters up to waters down. While the valve no ventee to the atmosphere, an internal escape would not consider a fugitive broadcast. By the contrary, an external escape means an escape from the interior of the valve to the environingingment, for example, through the vástago or of the closing of the body. While the escapes suppose a danger for the environingingment, are fugitive broadcasts.
According to an article of the publication Sealing Technology, the fugitive broadcasts all over the world add more than one million metric tonnes by year. In a recent study, carried out by the European Association of Enclosures, the broadcasts of escapes in valves, pumps and bridas in the plants of EE UU are responsible of losses estimated in 300.000 tonnes by year only in the chemical and petrochemical industry. The same study indicates that a third of all the broadcasts are fugitive broadcasts, and the half of them come from of valves.

The external escapes of racores, valves and other components of systems of fluent can convert to measure that passes the year in financial losses cuantiosas. For example, for a plant with 50.000 racores, the cost annual average because of escapes estimates in more than 25.000 dollars. These examples plead for an approach of total cost in the design, selection of product and maintenance of systems of fluids.
In east articulate, will centre us in escapes of individual components, particularly of escapes in valves of ball, a type of valve widely used and that allows effective enclosures and of big capacity of discharge in a lot of industries, like the chemicals, petrochemical, exploration of oil and gas, power and alternative fuels.
To control the fugitive broadcasts in valves of ball, is critical to select the correct valve for the application. It is necessary to begin with a suitable information on the application: ranks of pressesure and temperature, cleaning of the half, frequency of ciclado, frequency wished of maintenance, maximum discharge of admissible escape, requirements of discharge and possible pollution. Afterwards, it is necessary to choose the most adapted technology to the parameters of work, loaning the attention been due to characteristic of design and operation as well as to the compatibility of materials. This article can not cover all the types of valves of ball, but we will centre us in two characteristics of design that are especially important in the control of broadcasts and in the total cost of property: the design of the closing of the body and the design of the closing of the vástago.
Design of the closing of the body
The two more common systems of closing of the body are the one of threaded type and by means of brida. Whereas the threaded type is a more resistant closing and allows pressesures of service higher, the closing by means of brida allows an easier maintenance and fast with the valve on line, which is an important advantage.
The threaded type consists in one or two threaded terminals that roscan in the body of the valve after having entered the ball and the closing of the seat. The area of closing of the terminal threaded is relatively small and by this reason is a very efficient closing, allowing estanquidad until pressesures of 689 or 1.378 bar (10.000 or 20.000 psig). Besides, the nature of this design allows to the manufacturer offer a wide range of final connections.
In the valves that employ the closing type brida, the body of the valve consists of three parts that join by means of bridas, together and pernos (Figure 1). Since the area of closing in these components is greater, this design involves usually pressesures of service lower. Like the bridas close by means of board, there are fewer geometrical restrictions in the material of closing, with what have a wider range of available materials.
The material of standard closing of the manufacturer is not always the best option. The designers of the system have to have special care in investigating the compatibility of the material of closing with the conditions of work of his system, considering all the options like material of boards, distinct types of together tóricas or empaquetaduras of Grafoil that can contribute a design of valve more robust. The pernos of the closing bridado would have to be of a material of quality, like stainless steel 316 of grain toughened, to ensure that it keeps a strength of closing adapted.
Further of the materials of closing, an advantage of the type bridado is the ease of maintenance. When they withdraw the pernos, the body of the valve can knock down, what facilitates the maintenance and avoid to have to disassemble the valve of the system to have access to the enclosures of the seat and of the body. To measure that the rules on broadcasts do more strict, the ease of maintenance and repair turn into factors more important.
The escapes can give no only through the points of closing, but through the materials of the body, as the ones of body melted. When specifying a valve, the designer would have to ask on the integrity of the material of the body, how has been inspected, if it is of smelting or mechanised. Which specifications of metal demands the manufacturer? What control of quality has implanted? A Certificate of Essay of Material (CMTR) provides a lot of answers to the most critical questions on the quality of the material of the body.
Design of the vástago
In a valve of ball, has to have a half to ensure that the fluid of the system, was liquid or gas, no escape between the vástago and the body. This is the function of the closing of the vástago. If there is a ciclado sufficiently frequent, all the enclosures of the vástago will finish wearing out, and this wear will cause an escape. Nevertheless, some enclosures are more effective that others for some applications. According to the application would have to take a deliberate decision regarding the type of vástago.
Empaquetadura Of the vástago of an alone piece
The most basic technology and primitive is the one who contributes a board of an alone piece that surrounds to the vástago. When it tightens the nut of the empaquetadura downwards, the board, usually of politetrafluoroetileno (PTFE) compresseses , filling up the spaces that there is between the vástago and the carcasa of the body.
Alas, the PTFE and other materials of empaquetadura similar can arrive to flow (cold flow or tendency of some materials to change his form in the time). This circumstance can aggravate with the pressesure or the temperature. In some cases, the material can arrive to extrudir in areas in which it was not foreseen, minando his effectiveness and causing the escape of the fluid of the system.
To compensate this extrusion in cold, can be necessary tighten the nut of the empaquetadura more often to increase the strength of compressesion in the closing of the vástago, sobretodo if the pressesure or temperature change or to measure that cicla the valve. That tighten additional increases the pressesure against the vástago, elevating the pair of performance of the valve —command harder. Even it can that the nut of the vástago do bottom on the body of the valve, point in which it has to change the empaquetadura.
This so basic technology requires frequent inspections and adjust; if no, there will be escape. Besides, for a no expert operator, no always is clear when it is necessary to adjust the empaquetadura.
To reduce the risk of fugitive broadcasts, the design of empaquetadura of an alone piece would have to reserve for applications where the changes of temperature or pressesure are minimum, the ciclado is limited, or where there will be a frequent inspection and regulate.
Empaquetadura Of two pieces type Chevron
An empaquetadura of two pieces type Chevron is an improvement concerning the design of an alone piece, and allows ranks of pressesure or temperature wider as well as a regular performance without an excessive wear.
An empaquetadura type Chevron consists in two boards fit, one inside the another. The transversal section of the two boards has triangular form. But joined, the two boards form a rectangular section (see Figure 2). To measure that the nut of the empaquetadura of the vástago transmits his strength, the two boards push one to the another in the diagonal where joint , what transmits the horizontal strength and uniformly against the vástago and the carcasa of the body. With a minimum pressesure of the nut of the empaquetadura, creates a closing between the vástago and the body.
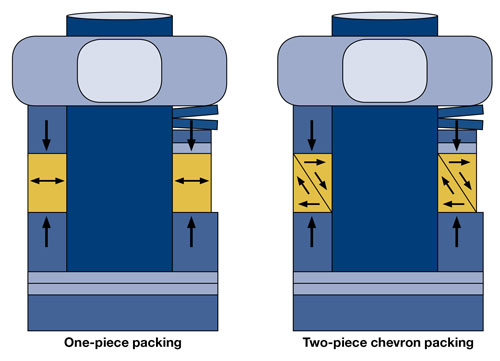
So that the closing Chevron seal properly, the two boards of PTFE have to keep in his place without extruir during the possible ciclados thermal sensors. The empaquetadura Chevron has to, therefore, be very contained and creame by the disks of support, that distribute the pressesure uniformly to the empaquetadura.
To reduce the need of inspection and adjust, the closing Chevron has to include also some disks Belleville, that act like docks that create a constant strength on the empaquetadura. This constant strength allows a uniform pressesure on the empaquetadura although there are changes in the pressesure or temperature. These docks provide a permanent strength against the closing and the body to ensure the correct quantity of strength of closing. To high temperatures, the docks compresses and leave space so that the empaquetadura expand . To low temperatures, the docks dilate and keep the correct pressesure on the empaquetadura. This system of empaquetadura autocompensante allows to the Chevron keep always a constant pressesure from the strength exerted by the docks. Like result, obtains a soft performance and a minimum wear of the empaquetadura. Without the docks, the empaquetadura would have to expand and contract in a relatively fixed space. When it dilated to high temperatures, the load in the vástago would increase and could extruir. The result would be a higher wear and performance harder.
Some designs of valves can allow that the pressesure of the system push the vástago upwards, and a mechanism autocompensante compensates this movement, as well as the dilatation and contraction of the empaquetadura, ensuring the constant pressesure.
The valves with closing of an alone piece can have docks and pretend be autocompensantes, but are not effective. The docks can allow contract or expand to the empaquetadura of PTFE to some extent, but without the design Chevron can not ensure a constant strength on the vástago. By definition, a valve with closing of an alone piece requires a strength of the dock on the empaquetadura very high, the quite so that it can deform it to out and create a closing. With performances repeated, the wear of the empaquetadura is considerable. The wear will comport to change often the empaquetadura and can ocasionar escapes.
Closing by means of board tórica
Another efficient technology of closing is the board tórica. When it is designed properly, this technology offers flexibility for applications that require high, drop or wide ranks of pressesure, for example, in a cylinder takes of sample, in which the pressesure can fall from the 158,5 bar (2.300 psig) when it is full, to the 6,9 bar (100 psig) when it was almost empty.
The board tórica is usually done of a very elastic material, as fluorocarbono FKM. Like the board Chevron of two pieces, the design of together tórica does not require of a lot of pressesure of the nut of empaquetadura; on the contrary, the own pressesure of the system transfers power to the board tórica, since when the pressesure increases, the board shapeless and increases his pressesure on the vástago. The other way around, when the pressesure of the gas diminishes, the board relaxles , filling the spaces between the vástago and the body. Thanks to his elasticity, the transversal section of the together tórica shapeless and reform to create the closing.
A suitable design of vástago with configuration of together tórica precise of a board of support or another mechanism, usually manufacturing with PTFE, that will contain the board under high pressesure. This board of support is designed to reduce the extrusion of the board tórica and keep it contained. If it allowed extruir to the board further of his limits, would break during the performance of the valve. This excessive extrusion could cause escapes and hamper the performance.
The design of board tórica is very effective to high pressesures. Regarding the temperature, pressesure or chemical attack, the design is limited by the specifications of the elastomer. The user has to ensure of the chemical compatibility between the fluid of the system and the elastomer.
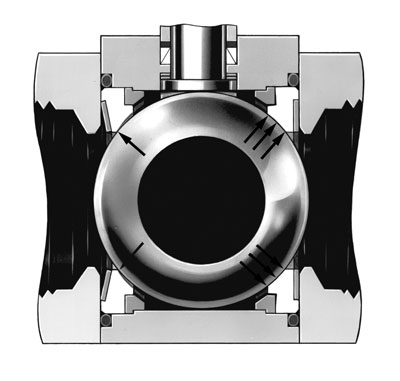
Misalignment of the vástago
Further of the relative problems to the design of the closing of the vástago, there are other causes of escapes in the vástago. They have to see with the alineación of the vástago. If by any reason the fuelle was pushed or forced lateralmente, could give an uneven wear in the closing of the vástago, causing escapes. There are two basic causes of misalignment.
In the first case, can be consequence of a wrong installation of the actuator. If the axis of the pneumatics actuator and the axis of the vástago are not properly ranged, the vástago will remain descentrado, causing a no uniform wear of the closing.
In the second case, a worn seat in the interior of the valve can cause this trip of the vástago. To understand this fact, owe first to review the basic anatomy of the valves of ball. These valves can use a design of floating ball or a design of trunnion.
In the design of floating ball, the ball is not fixed inside the body but it floats between two seats. In the enclosed position (Figure 3), the ball closes against the seat in the side of low pressesure, pushed waters down by a positive differential pressesure.

By the contrary, the design trunnion employs a ball also, but his geometry contains two cylinders —this geometrical figure receives the name of trunnion— fixed to the ball in his top and inferior (Figure 4). This component is lodged in the interior of the valve and can not displace in the sense of the discharge (does not float). When the ball turns to the positions of enclosed or open, turns solidariamente with the trunnions, that remain subject by means of casquillos and threads.
In the case of differential pressesures very high through the seat, a floating ball is pushed waters down… with too much strength. If there is not a design of seat advanced —like a seat compensated with docks, with board and dock in each side—, is possible that the ball do not go back to his central position. In consequence, the vástago remains displaced lateralmente and, over time, will cause an uneven wear of the closing of the vástago.
The design trunnion avoids an excessive trip of the ball water down. The trunnions, that keep in his place, keep the ball centred and the vástago ranged properly. Even with a hit of ariete, in which a fluid no comprimible like the water produces a brusque rise of pressesure, the trunnion will remain centred.
Conclusion
The aim of this article is not to plead for a design or another, by a design of floating ball or trunnion, for example. Each design has his suitable application. This article tries to show that the different designs have his strong points and these have a direct effect on the fugitive broadcasts. When choosing a valve, the designer of the system has to consider the compatibility of materials, pressesures, temperatures, frequency of inspection and adjust wished, and frequency of performance. Besides, when the cost is a factor determinante to select a valve, the designer of the system has to know the problems that can be entering in the system. The real cost of a valve is not the price of purchase but his total cost of property. With costs of upward prime matter and with sanctions more severe by incumplimientos environingingmental, have to consider all the direct and indirect costs associated with the maintenance, failure and spare.




























































































